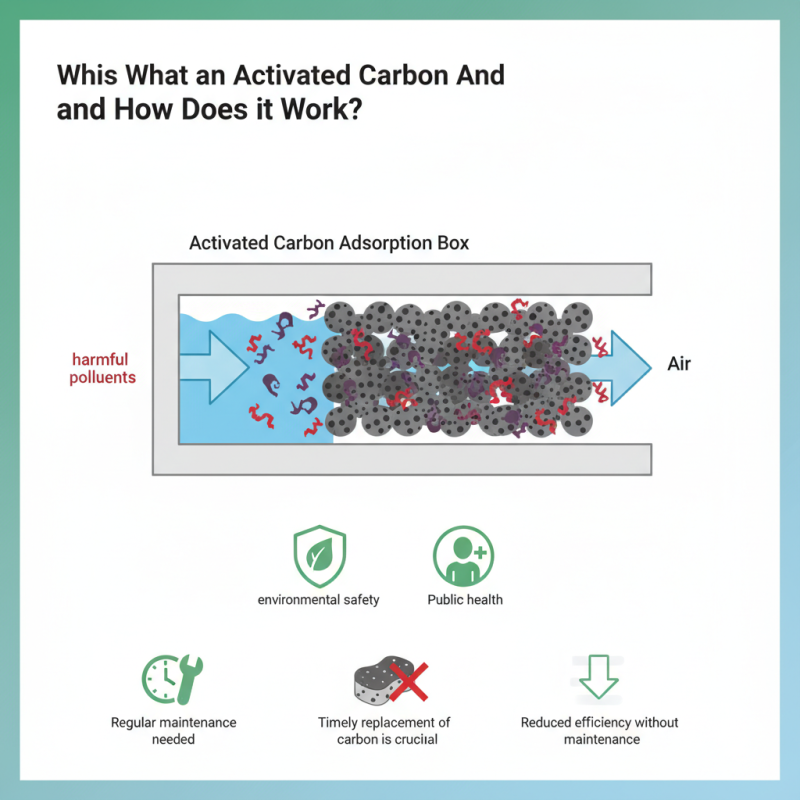
The Activated Carbon Adsorption Box is a vital tool in air and water purification. It utilizes activated carbon to capture harmful pollutants. This process enhances environmental safety and promotes public health.
Within the box, activated carbon acts like a sponge, attracting and holding onto contaminants. The porous structure increases its surface area, making it efficient. As air or water passes through, pollutants stick to the surface of the carbon. This method is effective for various applications, including industrial and residential uses.
Despite its efficiency, the Activated Carbon Adsorption Box has limitations. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance. Some users may overlook the need for timely replacement of carbon. This oversight can reduce efficiency and effectiveness. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing the benefits of this technology.
Activated carbon plays a crucial role in environmental engineering. Its porous nature allows it to adsorb a variety of pollutants from air, water, and soil. According to a report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), activated carbon can remove over 99% of certain contaminants from water sources. This makes it invaluable in treating drinking water and industrial effluents.
Activated carbon works through adsorption, capturing impurities onto its surface. This process is effective for various contaminants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals. In a study conducted by the American Water Works Association, activated carbon filters significantly reduced harmful substances in wastewater, proving their effectiveness in modern environmental practices.
Tip: Regular maintenance of activated carbon systems is essential. Over time, the adsorption capacity diminishes. Replacing or regenerating activated carbon ensures optimal performance.
Moreover, while activated carbon is highly effective, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each application may require specific configurations and treatments. Critics often point out the need for continuous research to address its limitations. It’s important to continue refining technologies to enhance the effectiveness of activated carbon in environmental management.
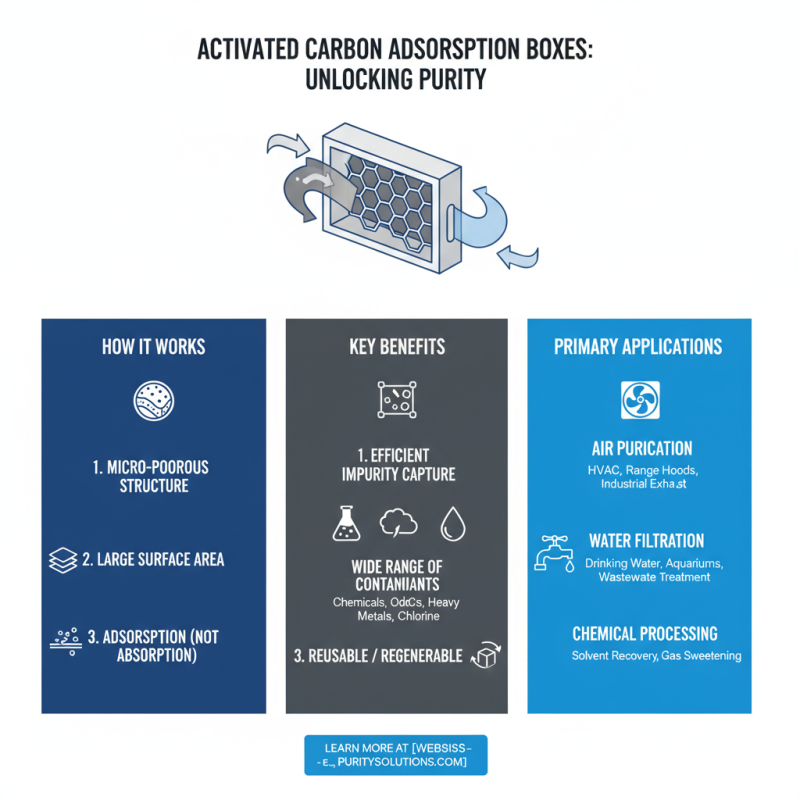
Activated carbon adsorption boxes are crucial in many applications. They effectively capture impurities and contaminants from air or water. But what makes them so efficient?
The mechanism of adsorption is key. Activated carbon has a vast surface area. Its porous structure allows for many particles to adhere. As air or liquid passes through, pollutants are trapped. This process relies on physical forces like van der Waals interactions. Unlike bonding, it doesn’t alter the chemical structure of pollutants.
Tips: Regularly check the activated carbon for saturation. Overuse can limit efficiency. Always ensure the air or liquid flows evenly through the box. Uneven flow can reduce adsorption effectiveness.
Another point to consider is the selection of activated carbon type. Not all carbon works for every contaminant. Some may be better for gases, while others excel in liquid environments. This choice can significantly impact performance. It’s worth doing research. Take some time to reflect on your specific needs. The right fit matters deeply.
Activated carbon adsorption boxes are essential tools in air purification. They effectively capture harmful gases and odors. The process begins when air flows through the box. As it passes, pollutants adhere to the surface of the activated carbon. This material has a high surface area, allowing it to attract various contaminants.
These boxes are widely used in indoor spaces. They find application in homes, offices, and industrial settings. For instance, they can reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from paints and cleaners. Additionally, they help eliminate smoke and pet odors, enhancing indoor air quality. However, their efficiency can diminish over time. Regular replacement or reactivation of the carbon is often necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Moreover, users should consider the limitations of these systems. Activated carbon mainly targets specific pollutants, but not all. Some chemicals may not be effectively captured. Therefore, combining these boxes with other air purification technologies can yield better results. Understanding the nuances of air purification can be complex, prompting the need for further exploration and research.

Activated carbon adsorption is influenced by various factors that determine its efficiency. The surface area of activated carbon is crucial. High surface areas, often exceeding 1000 m²/g, enhance adsorption capacity. A recent study noted that the pore size distribution can significantly affect contaminant capture. Smaller pores may trap certain molecules better, while larger pores work for bigger particles.
Adsorbate molecular characteristics also play a vital role. Molecule size, polarity, and structure affect how well they adhere to activated carbon surfaces. For instance, hydrophobic compounds tend to have higher adsorption rates on carbon surfaces, as shown in data from environmental processing reports. Additionally, temperature and pH of the solution must be considered. Optimizing these parameters can enhance adsorption efficiency by ensuring molecules interact effectively with porous structures.
Moreover, operational factors like contact time and concentration levels should not be overlooked. Reports indicate that insufficient contact time can lead to underperformance, failing to reach equilibrium. Challenges remain in achieving the perfect balance among these variables to optimize adsorption. Fine-tuning is essential, and ongoing research continues to explore these dynamics.
Activated carbon is a versatile material widely used for adsorption purposes. Different types of activated carbon possess varying adsorption capacities. These differences can impact their effectiveness in specific applications. The main types include granular activated carbon (GAC), powdered activated carbon (PAC), and extruded activated carbon (EAC).
GAC has large surface areas, making it suitable for water and air purification. Its larger particles allow for easier water flow. However, its lower adsorption capacity compared to PAC can be a shortfall in certain scenarios.
PAC, on the other hand, is highly effective due to its fine particles, enabling it to capture pollutants quickly. Yet, its rapid saturation can require more frequent replacements.
When choosing between these types, consider your needs. The right type can significantly enhance purification efficiency. Tips: Always test the carbon’s adsorption capacity beforehand. Monitor your system for any signs of exhaustion. Be prepared for occasional adjustments; perfection is not guaranteed.






